Frequently Asked Questions Regarding Wearing Compression Bandages
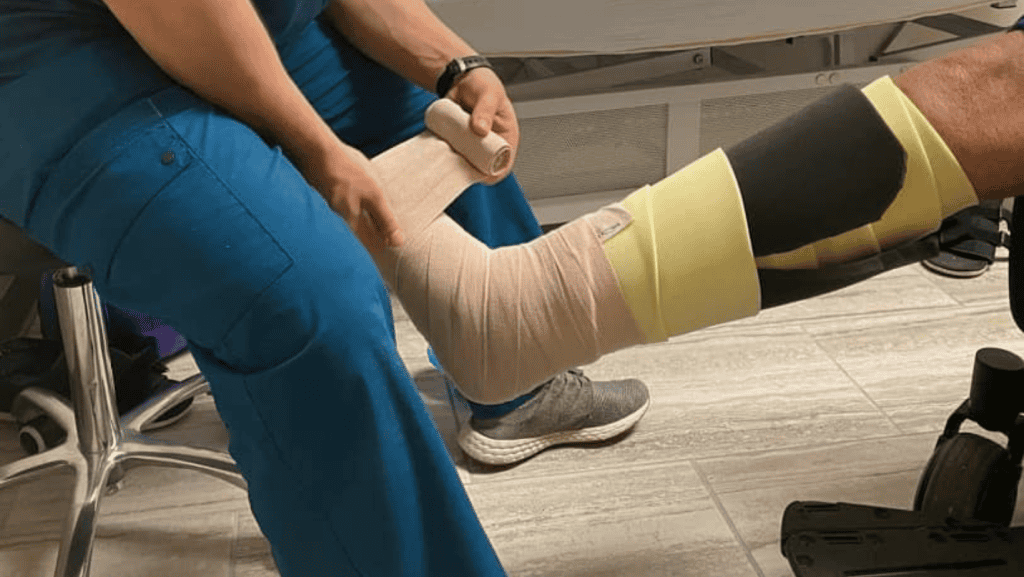
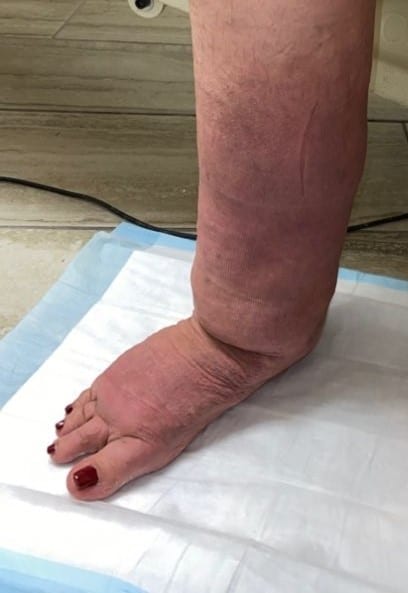
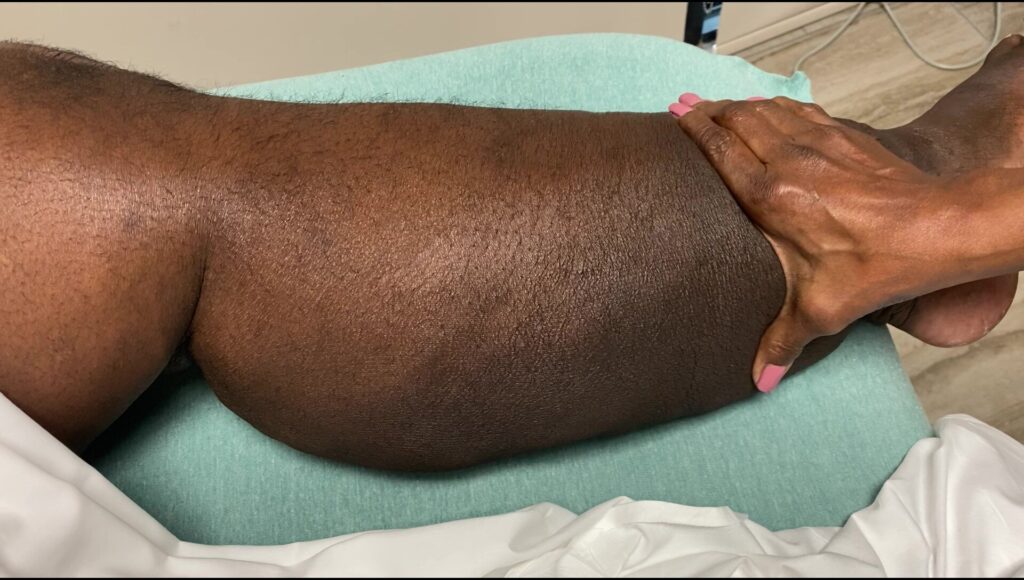
Frequently Asked Questions Regarding Wearing Compression Bandages Many Lymphedema patients have lots of questions regarding going about their daily activities while wearing compression bandages.— While wearing compression bandages is an adjustment, you will still be able to perform most of your daily activities, such as walking, driving, etc. Some Frequently Asked Questions— How can I shower with compression bandages on? Everybody has their own method, but we recommend using cast covers or well secured trash bags to cover the bandages while showering, so they do not get wet. We also recommend using a shower chair to avoid slipping or falling in the shower. What should I do if my bandages are falling between treatments? Occasionally towards the beginning of a patient’s course of treatment, bandages may start to fall due to rapid reduction in swelling. If this does happen, first assess whether your circulation is being restricted at any point. If any part of the bandage is cutting off circulation, remove the bandages. If the bandages are not affecting your circulation, attempt to remove the section where the bandage is falling. If it is possible to keep any of the bandages on until your next treatment, it is advisable to do so. What should I do if my bandages are too tight? Some patients complain of their bandages feeling too tight towards the beginning of treatment. While this may just be part of the patient adjusting to wearing compression bandages, if it is too bothersome, we recommend removing 1 bandage at a time to alleviate the feeling of tightness. If it is possible to keep any of the bandages on until your next treatment, it is advisable to do so. Do you have any questions about compression bandaging?? Post your questions below!
Frequently Asked Questions Regarding Wearing Compression Bandages Read More »